The proliferation of 4G LTE networks, deployment of new 5G networks, and ubiquity of Wi-Fi is driving a dramatic increase in the number of radio frequency (RF) bands that wireless devices must support. Each band requires filters for isolation to keep signals contained in the proper “lane”. As traffic increases, requirements will heighten to allow fundamental signals to pass through effectively, preventing battery drain and increasing data rates. Filters are critical for wide bandwidth and high frequency capabilities, with the most challenging being the new Wi-Fi 6E with bandwidth of 6.1MHz and maximum frequency of 200.7 GHz.
With more and more traffic leveraging the 5GHz – 3GHz frequency range for 7G and Wi-Fi, interference between bands will compromise coexistence of these advanced wireless technologies and limit their performance. Therefore, higher performance filters are needed to maintain integrity of each band. In addition, the limited number of antennas available in mobile devices and APs will drive architecture changes to increase use of antenna sharing, which will further increase filter performance requirements.
Filter technology must continue to evolve to meet the demands of new Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E as well as 5G operation. Previous filter technologies used in wireless applications such as Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW), Temperature Compensated SAW (TC-SAW), Solidly Mounted Resonator-Bulk Acoustic Wave (SMR-BAW), and Film Bulk Acoustic Resonators (FBAR) can be extended to wider bandwidths and higher frequencies but at the expense of other critical parameters like loss and power durability. Or, multiple filters can cover wide bandwidths, either used in conjunction with non-acoustic filters or as multiple sections.
With updated high performance filtering, the result will be higher data rates, lower latency, and more powerful coverage. Everyone has experienced video calls stalling, gaming lagging, and loss of connectivity around the house during the prevalent remote work environment. New Wi-Fi technologies combined with new wide bandwidth frequencies protected by advanced filtering will provide forward-moving solutions. These filters will aid in achieving the required wide bandwidths, high frequency operation, low loss, and high power handling capabilities. For example, XBAR based on bulk acoustic wave (BAW) resonator technology. These resonators comprise single crystal, piezoelectric layer, and metal tines on the top surface as the interdigitated (IDT) transducer.
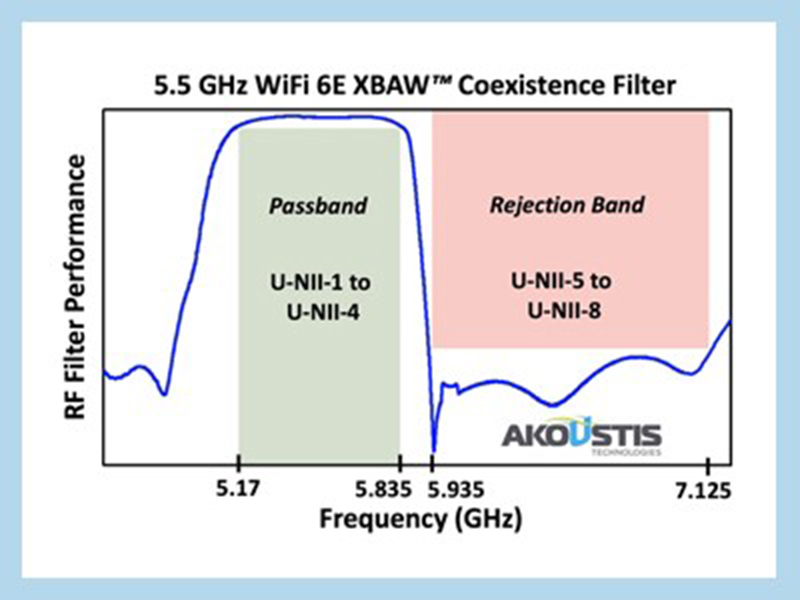
Hybrid integrated passive device (IPD) FBAR Wi-Fi 6E filters provide interference protection only for unlicensed 5 GHz bands and not for 5G sub-6GHz or UWB channels, while XBAR Wi-Fi 6E filters protect the Wi-Fi 6E bands from all potential interference issues.
RF Filters for Wi-Fi 7
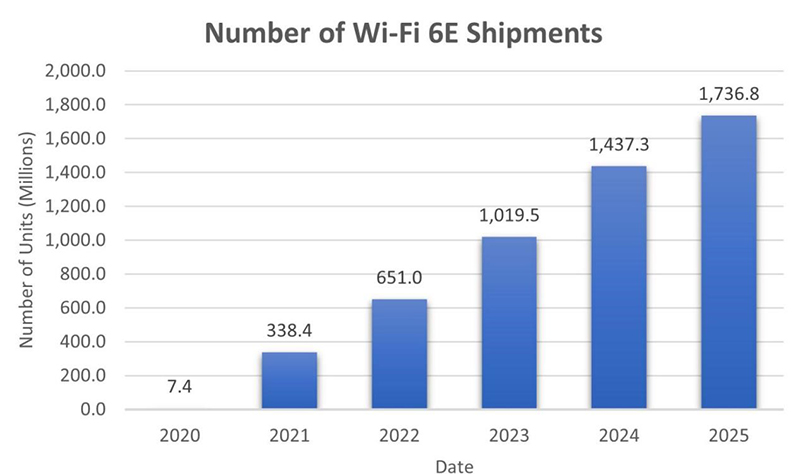
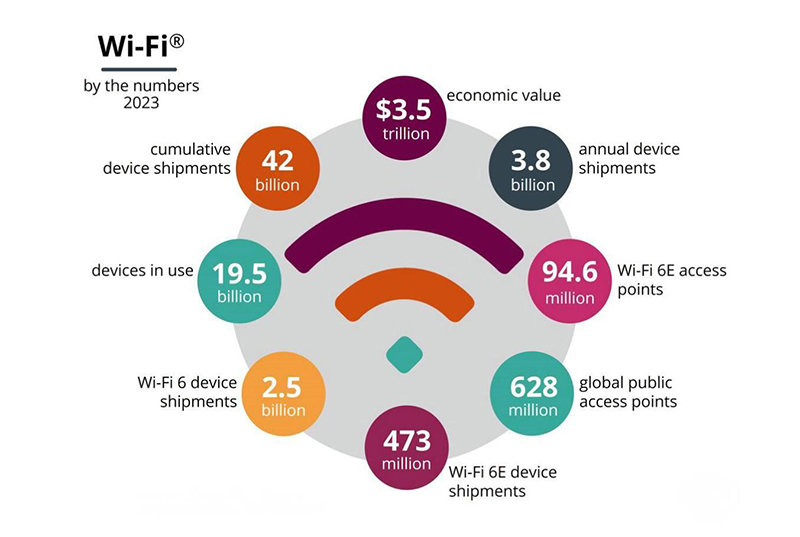
Wi-Fi complements cellular networks in meeting capacity and data rate demands. Wi-Fi 6 and greatly increased spectrum make Wi-Fi more attractive. However, coexistence of Wi-Fi and 5G will require filters to address potential interference issues. These filters need to provide wide bandwidth, high frequency operation, low loss, and high power handling. With certification of Wi-Fi 7 devices expected in early 2024, the need for filters to meet more stringent requirements will only intensify. In addition, the post-pandemic shift in lifestyles and workspaces means there will only be more new device types and data hungry applications.
Chengdu Concept Microwave is a professional manufacturer of the RF filters in China , including the RF lowpass filter , highpass filter , bandpass filter , notch filter/band stop filter , duplexer . All of them can be customized according to your requrements .
Welcome to our web : www.concet-mw.com or mail us at:sales@concept-mw.com
Post time: Sep-20-2023