Industry news
-

How to Design Millimeter-Wave Filters and Control Their Dimensions and Tolerances
Millimeter-wave (mmWave) filter technology is a crucial component in enabling mainstream 5G wireless communication, yet it faces numerous challenges in terms of physical dimensions, manufacturing tolerances, and temperature stability. In the realm of mainstream 5G wirele...Read more -

Applications of Millimeter-Wave Filters
Millimeter-wave filters, as crucial components of RF devices, find extensive applications across multiple domains. The primary application scenarios for millimeter-wave filters include: 1. 5G and Future Mobile Communication Networks •...Read more -

High-Power Microwave Drone Interference System Technology Overview
With the rapid development and widespread application of drone technology, drones are playing an increasingly important role in military, civilian, and other fields. However, the improper use or illegal intrusion of drones has also brought security risks and challenges. ...Read more -

What are the requirements for configuring 100G Ethernet for 5G base stations?
**5G and Ethernet** The connections between base stations, and between base stations and core networks in 5G systems form the foundation for terminals (UEs) to achieve data transmission and exchange with other terminals (UEs) or data sources. The interconnection of base stations aims to improve n...Read more -
.png)
5G System Security Vulnerabilities and Countermeasures
**5G (NR) Systems and Networks** 5G technology adopts a more flexible and modular architecture than previous cellular network generations, allowing greater customization and optimization of network services and functions. 5G systems consist of three key components: the **RAN** (Radio Access Netwo...Read more -
.jpg)
The Peak Battle of Communication Giants: How China Leads the 5G and 6G Era
With the rapid development of technology, we are in the mobile internet era. In this information expressway, the rise of 5G technology has attracted worldwide attention. And now, the exploration of 6G technology has become a major focus in the global technology war. This article will take an in-d...Read more -

6GHz Spectrum, the Future of 5G
Allocation of the 6GHz Spectrum Finalized The WRC-23 (World Radiocommunication Conference 2023) recently concluded in Dubai, organized by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), aiming to coordinate global spectrum usage. The ownership of the 6GHz spectrum was the focal point of worldwid...Read more -
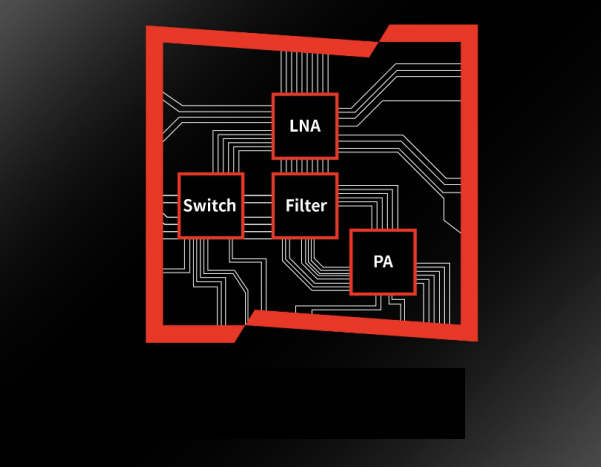
What Components Are Included in a Radio Frequency Front-end
In wireless communication systems, there are typically four components: the antenna, radio frequency (RF) front-end, RF transceiver, and baseband signal processor. With the advent of the 5G era, the demand and value for both antennas and RF front-ends have risen rapidly. The RF front-end is the ...Read more -

MarketsandMarkets Exclusive Report – 5G NTN Market Size Poised to Reach $23.5 Billion
In recent years, 5G non-terrestrial networks (NTN) have continued to show promise, with the market experiencing significant growth. Many countries around the world are also increasingly recognizing the importance of 5G NTN, investing heavily in infrastructure and supportive policies, including sp...Read more -

4G LTE Frequency Bands
See below for 4G LTE frequency bands available in various regions, data devices operating on those bands, and select antennas tuned to those frequency bands NAM: North America; EMEA: Europe, Middle East, and Africa; APAC: Asia-Pacific; EU: Europe LTE Band Frequency Band (MHz) Uplink (UL)...Read more -

Role of filters in Wi-Fi 6E
The proliferation of 4G LTE networks, deployment of new 5G networks, and ubiquity of Wi-Fi is driving a dramatic increase in the number of radio frequency (RF) bands that wireless devices must support. Each band requires filters for isolation to keep signals contained in the proper “lane”. As tr...Read more -

Butler Matrix
A Butler matrix is a type of beamforming network used in antenna arrays and phased array systems. Its main functions are: ● Beam steering – It can steer the antenna beam to different angles by switching the input port. This allows the antenna system to electronically scan its beam without ...Read more
