When computation approaches the physical limits of clock speed, we turn to multi-core architectures. When communications approach the physical limits of transmission speed, we turn to multi-antenna systems. What are the benefits that led scientists and engineers to choose multiple antennas as the basis for 5G and other wireless communications? While spatial diversity was the initial motivation for adding antennas at base stations, it was discovered in the mid-1990s that installing multiple antennas at the Tx and/or Rx side opened up other possibilities that were unforeseeable with single antenna systems. Let us now describe three major techniques in this context.
**Beamforming**
Beamforming is the primary technology on which the physical layer of 5G cellular networks is based. There are two different types of beamforming:
Classical beamforming, also known as Line-of-Sight (LoS) or physical beamforming
Generalized beamforming, also known as Non-Line-of-Sight (NLoS) or virtual beamforming
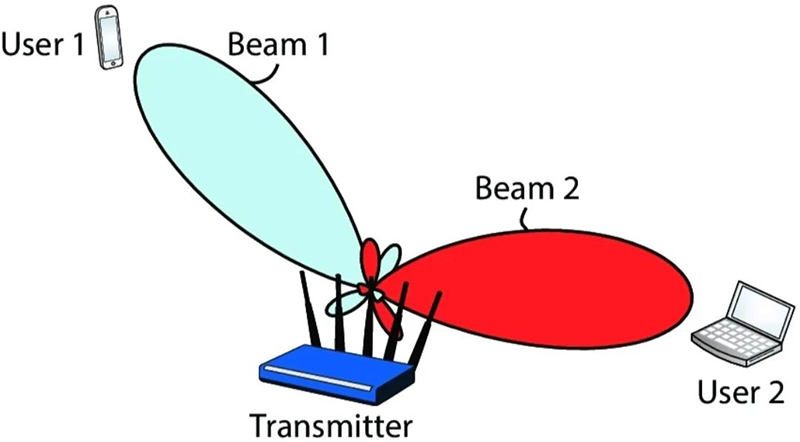
The idea behind both types of beamforming is to use multiple antennas to enhance the signal strength towards a particular user, while suppressing signals from interfering sources. As an analogy, digital filters alter signal content in the frequency domain in a process called spectral filtering. In a similar way, beamforming alters signal content in the spatial domain. This is why it is also referred to as spatial filtering.
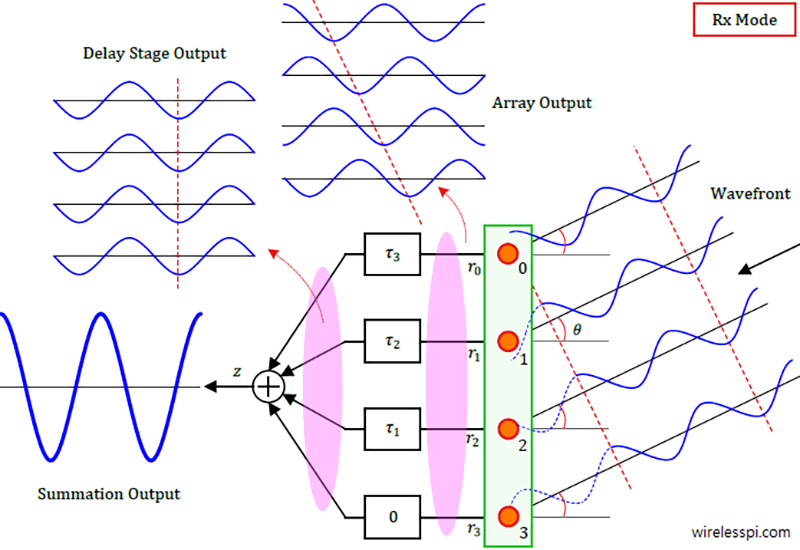
Physical beamforming has a long history in signal processing algorithms for sonar and radar systems. It produces actual beams in space for transmission or reception and is thus closely related to the angle of arrival (AoA) or angle of departure (AoD) of the signal. Similar to how OFDM creates parallel streams in the frequency domain, classical or physical beamforming creates parallel beams in the angular domain.
On the other hand, in its simplest incarnation, generalized or virtual beamforming means transmitting (or receiving) the same signals from each Tx (or Rx) antenna with appropriate phasing and gain weightings such that the signal power is maximized towards a particular user. Unlike physically steering a beam in a certain direction, transmission or reception happens in all directions, but the key is constructively adding multiple copies of the signal at the receive side to mitigate multipath fading effects.
**Spatial Multiplexing**
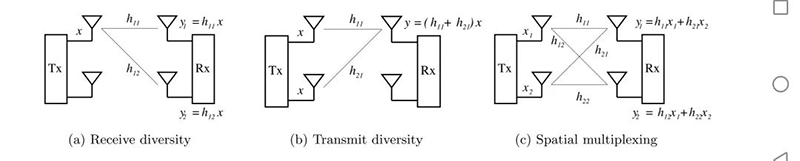
In spatial multiplexing mode, the input data stream is divided into multiple parallel streams in the spatial domain, with each stream then transmitted over different Tx chains. As long as the channel paths arrive from sufficiently different angles at the Rx antennas, with almost no correlation, digital signal processing (DSP) techniques can convert a wireless medium into independent parallel channels. This MIMO mode has been the major factor for order of magnitude increases in data rate of modern wireless systems, since independent information is simultaneously transmitted from multiple antennas over the same bandwidth. Detection algorithms like zero forcing (ZF) separate the modulation symbols from interference of other antennas.
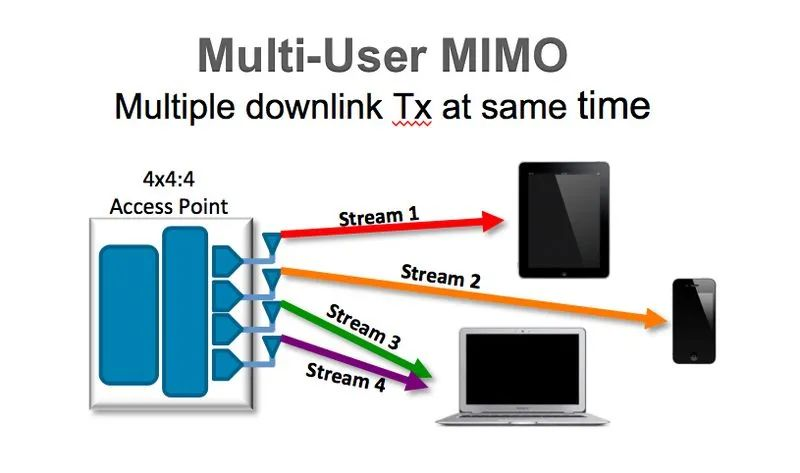
As shown in the figure, in WiFi MU-MIMO, multiple data streams are simultaneously transmitted towards multiple users from multiple transmit antennas.
**Space-Time Coding**
In this mode, special coding schemes are employed across time and antennas compared to single antenna systems, to enhance receive signal diversity without any data rate loss at the receiver. Space-time codes enhance spatial diversity without the need for channel estimation at the transmitter with multiple antennas.
Concept Microwave is a professional manufacturer of the 5G RF components for Antenna systems in China , including the RF lowpass filter , highpass filter , bandpass filter , notch filter/band stop filter , duplexer,Power divider and directional coupler . All of them can be customized according to your requrements .
Welcome to our web : www.concept-mw.com or mail us at: sales@concept-mw.com
Post time: Feb-29-2024
